With ISO 9001:2015 comes a push for leaders to make quality a top priority for every employee—not just the ones directly involved in quality management. But what does it really mean to make quality an underlying part of all business operations?
The shift to risk-based thinking under ISO 9001:2015 is supported by 7 key quality management principles—customer focus, leadership, engagement of people, process approach, improvement, evidence-based decision making and relationship management.
Consult a quality expert today and discover how ETQ Reliance can streamline your shift to risk-based thinking.
1. Quality Management and Customer Focus
The ultimate focus of quality management is to meet and exceed customer expectations. This means treating every customer interaction as an opportunity to deliver more value, increasing repeat business, revenue and your brand’s reputation in the process.
- Connect organizational objectives to current and future customer expectations
- Actively manage customer relationships for long-term success
- Monitor customer satisfaction and proactively address issues
- Enable direct feedback from customers to reduce the time to respond to issues
7 key quality management principles—customer focus, leadership, engagement of people, process approach, improvement, evidence-based decision making and relationship management.
2. Quality Management and Leadership
Unify the purpose and direction of your workforce and create productive environments for all employees to pursue quality objectives. When strategies and processes are aligned across all departments, you’re able to meet quality objectives more efficiently, maximize collaboration across business functions and coordinate your operations around risk-based thinking. Quality shouldn’t be thought of as an “add-on” or separate process; rather, quality should just be the norm for how the organization operates.
- Communicate your mission, vision, strategy, policies and processes clearly across the organization
- Build a culture of quality that’s rooted in trust and integrity
- Recognize and reward the contributions that people make toward organizational quality
3. Quality Management and Engagement of People
Effectively and efficiently managing quality at all levels of your organization requires deep trust and respect for all employees and stakeholders. Recognizing, empowering and enhancing the competence of your people will increase their understanding of quality objectives, maximize their attention to the quality culture and improve professional development.
- Ensure employees understand the importance and value of their contributions
- Empower people to take initiative and promote the quality culture without fear
- Conduct regular surveys to assess workforce satisfaction and response appropriately
- Celebrate identifying and fixing quality issues
4. Process Approach
A electronic quality management system (EQMS) includes a wide array of inter-related processes to produce consistent and predictable results. When all stakeholders have a deep understanding of how the QMS produces results, you’re able to focus more effectively on opportunities for improvement, optimize cross-functional performance and convey confidence to partners that you’ll provide consistent quality.
- Define objectives clearly and create formal processes to achieve them
- Understand process interdependencies and analyze the impact of any changes
- Address risk proactively to optimize the overall outcomes of quality management
- Involve everyone in defining and understanding your processes – including not just your internal teams, but external parties such as suppliers, as well
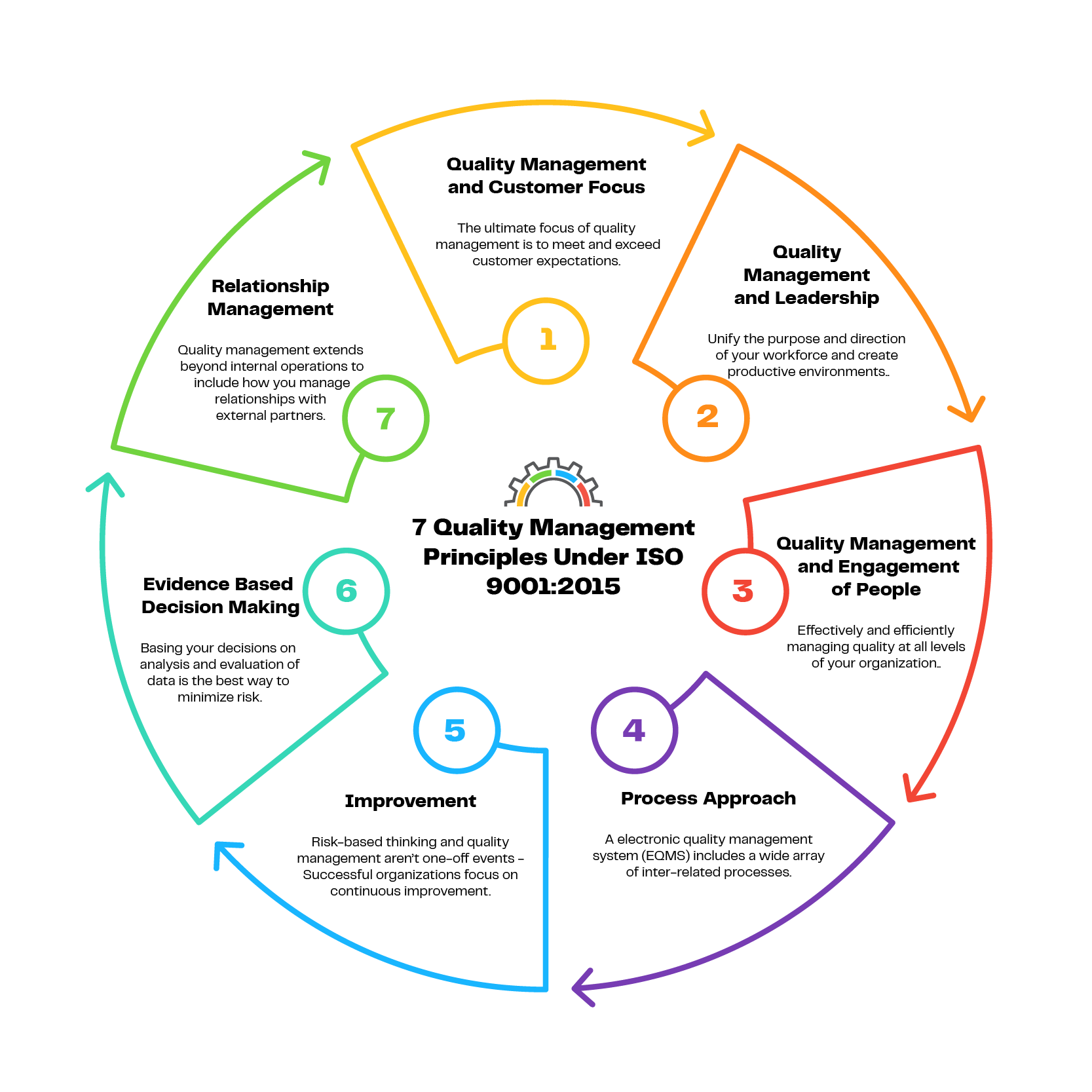
5. Improvement
Risk-based thinking and quality management aren’t one-off events. Successful organizations focus on continuous improvement to streamline root-cause investigations, enhance the drive for innovation and boost your ability to anticipate and react to both internal and external opportunities.
- Educate and train all levels of employees to run basic quality management tools and methodologies
- Connect improvement considerations to the development of new products
- Deploy specific processes to execute improvement projects across your organization
- Measure the results – employee training, process improvements, quality levels
6. Evidence-Based Decision Making
All decision making involves some level of uncertainty. But basing your decisions on analysis and evaluation of data is the best way to minimize risk. Evidence-based decision making will help you maximize operational efficiency, assess process performance effectively and gain a deeper understanding of potential unintended consequences.
- Develop a centralized location for all data to provide a single source of truth
- Provide easy access to all necessary data to those that need it
- Modernize approaches to analyzing and evaluating data quality
- Strike a balance between evidence, experience and intuition when making decisions
Strike a balance between evidence, experience and intuition when making decisions
7. Relationship Management
Quality management extends beyond internal operations to include how you manage relationships with external partners like your suppliers. Effectively managing partner relationships will increase your ability to deliver value to customers, support an efficient supply chain and enhance the overall performance of your organization.
- Map out all relevant relations with suppliers, partners, customers and investors
- Define KPIs and goals for each relationship
- Prioritize relationship management based on quality impact
- Measure the performance of each relationship and provide feedback to partners


